Unfortunately, back surgery can fail to relieve your symptoms, or you may even develop a new set of problems afterward. Our specialty team explains what might have gone wrong and how they address failed back surgery.
While it’s rarely the first, second, or even third choice for painful spinal conditions, there are times when back surgery or neck surgery becomes your best treatment option for relieving discomfort and restoring mobility. But what happens when spine surgery doesn’t help? Even worse, what if you develop new symptoms after the procedure?
The team of top-tier specialists at Spine Center Atlanta, serving their Georgia communities from multiple locations, have significant experience in solving spinal conditions that affect your quality of life. Read what the Spine Center team says about failed back surgery, why it happens, and how they can help.
Understanding failed back surgery
Surgeons generally recommend back surgery with the expectation that, following a period of healing and rehabilitation, the procedure will relieve your symptoms, restore mobility, and improve your overall quality of life.
Failed back surgery (FBS) occurs when your back pain and other symptoms return after surgery, or the procedure never adequately resolved your problems, or your condition evolves to include new symptoms, such as neuropathic pain traveling into your legs or arms.
What causes failed back surgery?
Common causes of failed back surgery include:
Adjacent segment disease (ASD)
ASD can occur after spinal fusion surgery, causing excessive movement in the spinal segments above or below the fused site. The movement accelerates degenerative changes, causing spinal instability and resulting in pain.
Scar tissue
Postsurgical back pain that develops within a few months of the procedure could be related to scar tissue irritating spinal nerve roots. Depending on the nerve’s location, this issue could cause pain, numbness, and muscle weakness in the buttocks, legs, neck, shoulders, or arms.
Pseudoarthrosis
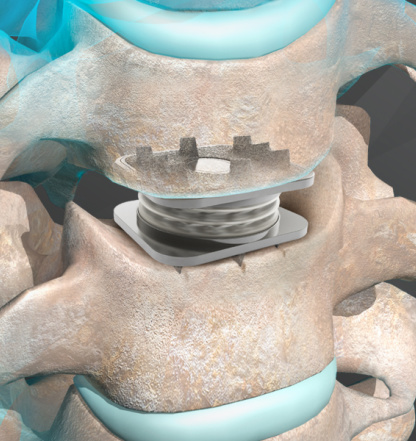
During spinal fusion, your surgeon uses bone cement to fuse two vertebrae together. Ideally, this prevents movement between vertebral bodies, stabilizes the spine, and resolves pain. Your surgeon may also attach metal plates, screws, or rods to help hold the spine in place.
Pseudoarthrosis is a possible complication of spinal fusion, occurring when the vertebrae fail to fuse. This nonunion can also cause the hardware used during spinal fusion to loosen or break.
Other potential causes of FBS include post surgical infection, inaccurate diagnosis before surgery, failure to complete rehab, or preexisting risk factors known to affect surgical outcomes, such as smoking or excess weight.
How do you treat failed back surgery?
Your Spine Center Atlanta specialist starts with a thorough evaluation that typically includes advanced diagnostic imaging studies to determine the cause of your symptoms. They also carefully review images taken before, during, and after your spine surgery and details regarding your postsurgical recovery and rehab process.
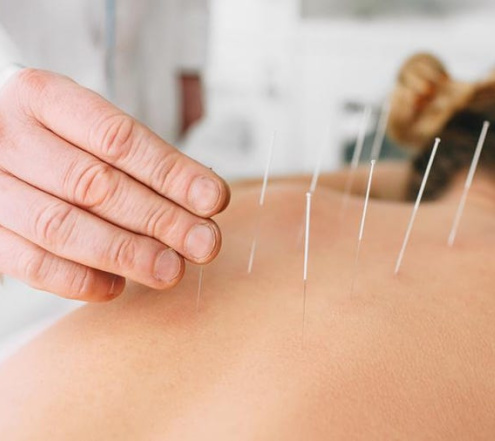
Customized treatment strategies to reduce pain and other symptoms related to FBS can include numerous nonsurgical treatments, including:
- Medication
- Physical therapy/rehab
- Neuromodulation (spinal cord stimulation)
- Epidural steroid injections to relieve inflammation and nerve irritation
- Regenerative medicine therapy
- Radiofrequency nerve ablation to block pain signals
Depending on the underlying cause of FBS, should these conservative therapies fail to resolve your symptoms, you may benefit from revision spine surgery.
Schedule an evaluation at Spine Center Atlanta today by calling the office or requesting an appointment online.